Apple Security Engineering and Architecture (SEAR) and the Citizen Lab opened a pair of critical vulnerabilities relating to the abuse of WebP images which could lead to exploitation of Google Chrome and Chromium-based browsers, as well as the webmproject/libwebp project by Google.
Overview of the WebP Vulnerability
|
CVE # |
Release Date |
CVSS Score |
EPSS Percentile |
Status |
|
12-Sep-2023 |
8.8 |
97% |
Active |
|
|
CVE-2023-5129 |
25-Sep-2023 |
10 |
N/A |
Rejected - Duplicated of CVE-2023-4863 |
CVE-2023-4863 is listed on CISA KEV (known exploited vulnerabilities) as being actively exploited; it was extended from Chromium-based browsers, to any application implementing libwebp. The libwebp project is used by many applications including the popular Electron framework. The vulnerability also extends to general purpose software and applications using libwebp.
Technical Analysis of CVE-2023-4863
The libwebp package was created by Google over a decade ago, with the library containing the functionality to render images in the .webp format.
WebP is an image format developed by Google that is offered as a better alternative to JPEG, PNG and GIF due to improved lossless and lossy compression, which results in web pages loading faster. Applications can support the WebP format using a library called libwebp.

The vulnerability can be potentially exploited using a maliciously crafted .webp lossless file which would lead to an out of bounds/overflow condition on the affected libwebp library.
Exploitation of the vulnerability could lead to Denial of service (DoS) of affected application to malicious remote code execution (RCE) on the impacted endpoint.
Why is this a challenge?
The libwebp packages are used in hundreds of applications — patching this is a challenge as updating application framework or re-compiling of applications requires thorough testing of applications prior to production release.
As such there is a time gap here which is advantageous to an attacker, as post exploitation a backdoor could be left open allowing stealthy and uncontrolled access to the environment.
Shortcuts on the patching cycle by skipping thorough validation can lead to business disruptions (compatibility issues and functionality losses) affecting revenue.
Visibility of usage of libwebp package in custom built applications is also an important aspect on building defense against exploitation of this vulnerability.
Vulnerable Applications
This sample list of vulnerable applications is extensive. A complete listing, which currently includes over 700 applications based on Electron can be found here.
|
Category |
Products |
|
Web Browsers |
Google Chrome, Safari, Microsoft Edge, Mozilla Firefox, Tor, Beaker (web browser), GNOME Web, Midori, OhHai Browser, Pale Moon, SEOBrowse |
|
Social Media |
Discord, Facebook, Instagram, Linked, ModernDeck for Twitter, Pinterest, Reddit, SpinShare Client, Telegram, Twitter, WhatsApp, Yammer |
|
Video Platforms |
Lbry, Twitch, Vimeo, YouTube, YTMDesktop App |
|
Graphics Software |
Aseprite, GIMP, Graphic Converter, ImageMagick, Paint.NET, Photoshop, Photoshop and Picasa, Pixelmator, XnView |
|
Cloud Storage |
Amazon Photos, Dropbox, Google Drive, Google Photos |
|
Ecommerce |
Amazon, Ebay, Etsy, Shopify, WooCommerce |
|
CMS |
Drupal, Joomla, MediaWiki, WordPress |
|
Email Services |
Gmail |
|
Forum Software |
PHPBB, vBulletin, XenForo |
|
Photo Editing |
GDAL, GIMP, Graphic Converter, ImageMagick, Paint.NET, Photoshop, Photoshop and Picasa, Pixelmator, XnView |
|
Game Engines |
Godot Engine, Unreal Engine, Unity |
|
Desktop Software |
1Password, Basecamp 3, Bitwarden, Blender, Cryptocat (discontinued), Discord, Discord RPC Maker, Electron App Store (Unofficial), Etcher, FastPictureViewer, Fifo FileCtor, Gitify, GitHub Desktop, GitKraken, Gnome Web, healthi, Inboxer, Joplin, Keybase, LibreOffice, Light Table, Logitech Options +, LosslessCut, Mattermost, Microsoft Office 2010, Microsoft Teams, Motrix, Museeks, Music Player, Obsidian, QQ (for macOS), Rambox, Signal, Skype, Slack, Spotify, Symphony Chat, Tabby, Termius, TIDAL, VLC Media Player, Visual Studio Code, WebTorrent, Windows Photo Viewer, Wire, Youtube Music for Desktop |
|
Mobile Apps |
Lyft, Telegram Messenger, Uber |
|
Web Servers |
Apache, IIS, nginx |
|
Developer Tools |
Advanced REST Client, Aeon, Antares, Appium Desktop, Barklarm, Believers Sword, Blockbench, BoxHero, Brim, Buttercup, Camunda Modeler, Cider, Clovery, Codex, Colorpicker, Cozy Desktop, CryptoARM GOST, Dat, DECK, DeckMaster, Deskfiler, Dict, Django, Doki Doki Mod Manager, Dopamine, DropPoint, Dusk Player, EBTCalc, ElectroCRUD, Electron App Store (Unofficial), Erin, ETCD Manager, Etcher, ExifCleaner, Fifo FileCtor, Fishing Funds, FLB Music, Flask, Frame, Gaucho, Gitify, gSubs, healthi, HexoClient, ImageShrinker, Inboxer, Invizi, itch, Jasper, Juggernaut, Kahla, Kap, KeeWeb, Knowte, Kube Dev Dashboard, Kube Forwarder, Laravel, Laravel Kit, Last Hit, LBRY Desktop, Lepton linked, Lisk Hub, lsdeer, Mailspring, Markdownify, massCode, mdp, mediaChips, Metronome Wallet, Mini Diary, MJML App, Monokle, monolith code, MongoDB Compass, MoviePrint, Mullvad, Netron, Network Status Check, nteract, nuclear, OhHai Browser, Oversetter, P3X Redis UI, PanWriter, asskey, Patchwork, Pencil, Picturama, PiTV, poi, Pomotroid, PreMiD, PrettyEarth, Primate Puppetry, Qawl, Quark, Quba E-Invoice Viewer, QuickRedis, R6RC, Rainbow Board, Rambox, Rebaslight, Recode Converter, Redis GUI (unofficial), RenderTune, React, Responsivize, Ride Receipts, Scratch For Discord, SeaPig, Serina, Silex website builder, SimpleInstaBot, Singlebox, Snippet Store, Socially, Soundnode, SpaceEye, SpinShare Client, Sqlectron, sqlui-native, Standard Notes, Standup Picker, Streamlabs OBS, Sturdy, Subtitler, Super Productivity, Switch, TagSpaces, Taskana, TextureLab, Thorium Reader, Time Series Admin, To Do, todometer, Transee, Translatium, Tropy, Tusk, Twinkle Tray, U Stair, Unfx Proxy Checker, Upcount, Vue.js, WebKitty, WizardMirror, wnr, yana, Zap |
|
Major Companies |
Facebook, Google, Slack, Wikimedia, WordPress.com |
|
Other Programs/Scripts |
Display-dj, Ffmpeg, GDAL, music-player, Musify, Notion, photoline, Picasa, React, Signal, Sumatra PDF, Vue.js |
List source: https://www.cyberkendra.com/2023/09/webp-0day-google-assign-new-cve-for.html
How Morphisec Helps
AMTD-Based Patchless Protection
As the vulnerability is an out of bounds/buffer overflow type, it is categorized under the in-memory type. Compensatory controls currently focus on developing IPS/IDS signatures to help identify/protect applications against exploitation. The current implementation of signatures works on the Network layer of the TCP/IP stack and as such the attackers, with minor modifications, can evade these protection mechanisms and exploit the applications.
Morphisec, by its implementation of Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD), alters the application memory structure during the load time and as such mitigates the vulnerable condition itself.
This differs significantly from the existing signature/behavior-based defense mechanisms and offers patchless protection for vulnerabilities.
Morphisec's AMTD technology provides organizations with credible patchless protection, and compensatory control to mitigate the risk exposure and reduce the attack surface of the application.
This provides the operations team the necessary time to effectively test and deploy the patches to mitigate the risk conditions.
Risk-based vulnerability prioritization
Adding to the compensatory control capabilities, Morphisec provides organizations visibility to the applications using the libwebp components, this also provides the team the ability to prioritize the patching strategy as Morphisec provides a usage-based scoring mechanism, thus providing a unique capability to identify affected applications based on actual usage.
Morphisec’s Risk-Based Vulnerability Prioritization provides a clear path to resolve the organization’s threat exposure with highly focused metrics including:
- EPSS Percentile Scoring: While most organizations rely on CVSS scoring, the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), combines multiple threat feeds and other data sources to create a probability score of a vulnerability being exploited in the wild. Currently with an EPSS percentile of 96% CVE-2023-4863 is at a high risk of exploitation. EPSS is a data-driven effort for estimating the likelihood (probability) that a software vulnerability will be exploited in the wild.
- Usage Based Scoring: Applications with intensive use are at a higher priority for patching versus an application with a high-risk score but isn’t actively in use.
- Host Exposure Scoring (HES): Patches must be updated on specific hosts (assets/devices). Business critical hosts, servers and workloads must be prioritized. Morphisec’s proprietary HES scoring aggregates cumulative vulnerabilities on specific devices, and allows grouping of devices by their criticality, facilitating clear focus to which devices are at risk.
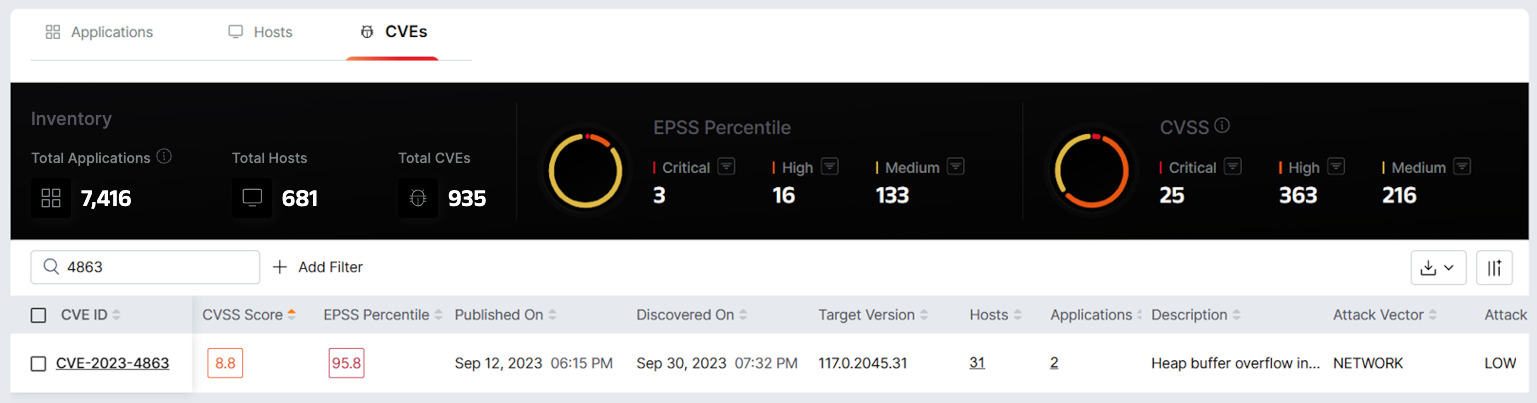
Morphisec’s Risk-Based Vulnerability Visibility dashboard displays the EPPS score of the vulnerability, with a clear mapping of effected hosts and applications.
As a layer in a defense-in-depth security posture, AMTD prevents zero-day, fileless, and in-memory attacks, offering true Defense-in-Depth for endpoint, server and workload protection, with a negligible performance impact, and with minimal overhead to the operations staff.
Want to learn more?
Morphisec is trusted by 7,000+ companies and prevents more than 30,000 attacks daily across more than nine million protected endpoints, servers and workloads on Windows and Linux devices. To learn more about the technology and why Gartner calls AMTD “the future of cyber,” read our white paper Zero Trust + Moving Target Defense: The Ultimate Ransomware Strategy.
Or, schedule a demo to see Morphisec in action.





.png?width=571&height=160&name=iso27001-(2).png)