Security leaders are acutely aware of vulnerability risks. Organizations continue to allocate thousands of dollars to periodic vulnerability assessments, and thousands more to technology and resources for mitigation — yet vulnerability-based breach events persist. According to the Verizon Data Breach Investigation Report (DBIR), more than half of reported breaches and ransomware attacks leverage vulnerabilities.
Recent examples include the WebP (libwebp) zero-day vulnerability which leverages WebP images to exploit Google Chrome and Chromium-based browsers, the MOVEit Transfer vulnerability which was actively exploited and still plaguing companies, and the CISA advisory on the “Citrix Bleed” vulnerability warned to be exploited by LockBit 3.0 ransomware affiliates.
More than 4,400 critical (CVSS score 9+) vulnerabilities have been published so far this year, impacting hundreds of applications. Triaging and patching this never-ending list of vulnerabilities is an arduous and overwhelming task for IT operations teams.
Furthermore, CVSS driven processes lack overall business context, don‘t define an organization’s exposure, and fail to appropriately align risks to patching efforts, leaving an organization unable to prioritize and mitigate its risk in a timely and cost-effective manner.
It is Important to note that less than 2% of published vulnerabilities are actively exploited and this is a fact that is not emphasized in current vulnerability management practices.
Standard vulnerability management practices aren’t enough
The success of cyber attackers in exploiting vulnerabilities is possible — in large part — due to shortcomings in standard vulnerability management and prioritization practices, which leave unpatched applications that can expose their organizations to attacks.
Here’s why:
- Patching gaps – Vulnerability remediation is a resource intensive process, leading to time gaps where organizations are exposed. Deploying security patches requires testing, and compatibility checks, creating a gap of 4-6 weeks and more to patching a vulnerability.
- Emergency patching without efficiently testing the patches presents potential risks and business impact —prioritization is crucial in this cycle to mitigate exposure before the rise of new vulnerabilities.
- Exposure and application usage across organizations vary — No two organizations have the same risk profile. For example, if an application with a high severity vulnerability is installed, the current process would focus on remediating the vulnerability by patching it. If usage of the application is considered, then this would provide the organization a more definite and accurate direction in mitigating risk rather than just patching the vulnerability and continuing the exposure life cycle management. Furthermore, applications used in critical business processes and services, especially in internet exposed applications, represent a greater risk than vulnerabilities residing in applications running within protected hosts.
- Standard vulnerability severity rankings don’t always represent risk — Current vulnerability management processes primarily rely on the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to assess the severity of a vulnerability and drive patching efforts, but a high severity ranking doesn’t necessarily indicate high risk. Actual risk depends on the usage of the applications, business context, and the exploitability potential of the vulnerability.
Ideally, patching efforts should be prioritized to vulnerabilities that have a high probability of exploitability, within the specific context and usage existing in each organization. This will reduce the burden on the IT Operations staff and the IT Risk team who generally need to spend an extended amount of time reviewing vulnerability assessment reports and then prioritizing which gaps need to be closed.
Thus, having a clear (and current) picture of a vulnerability’s risk to the organization helps teams better prioritize and optimize patching efforts.
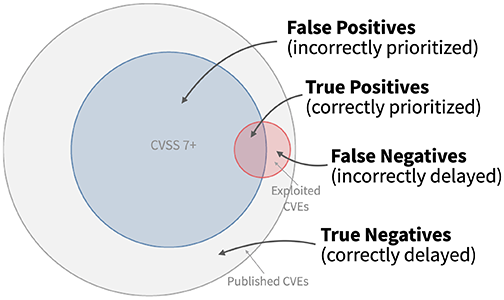 Exploited vulnerabilities represent a small percentage of all published CVEs. Patching driven by primarily by CVSS scoring can lead to incorrect prioritization efforts. Image source: first.org
Exploited vulnerabilities represent a small percentage of all published CVEs. Patching driven by primarily by CVSS scoring can lead to incorrect prioritization efforts. Image source: first.org
Morphisec's Risk Based Vulnerability Prioritization
Morphisec’s next generation vulnerability prioritization empowers organizations with continuous, business context and risk-driven remediation recommendations, enabling effective prioritization of patching processes, while reducing exposure with patchless protection, powered by Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD).
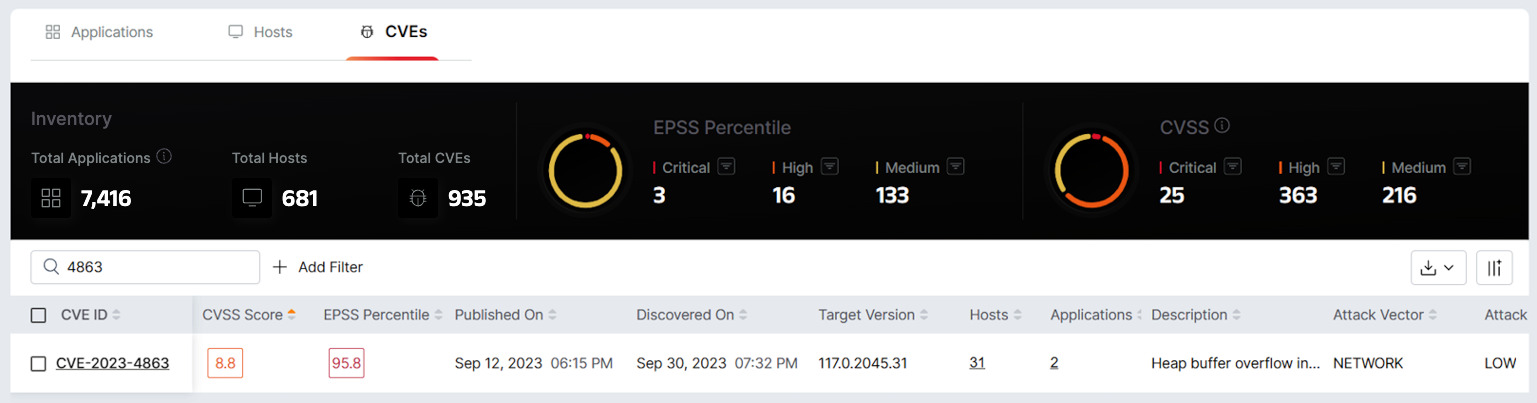
Morphisec’s risk-based vulnerability prioritization showing results for CVE-2023-4863 (libwebp)
Key Capabilities
- Business Context Risk Prioritization: Grouping and prioritization of risk according to business functions, services, and critical assets, for example: web-facing applications, databases, financial transaction systems, and systems containing PII and corporate IP.
- Host Exposure Scoring (HES): Morphisec’s proprietary HES scoring represents the aggregated value of all vulnerabilities on each host/device based on criticality, exploitability, usage, and exposure, facilitating clear prioritization of vulnerability remediation efforts.
- Application Driven Risk Prioritization: Enables organizations to execute remediation efforts according to the most exposed applications, mapping their attached CVEs and impacted hosts. Morphisec’s proprietary dashboards aggregate application risk in the event of multiple vulnerabilities, enabling effective prioritization.
- Exploitability Driven Prioritization using EPSS and CISA KEV:
-
- Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS): Combines multiple threat feeds and other data sources to create a probability score of a vulnerability being exploited. EPSS is a data-driven effort that is continuously updated based on the existence of exploit POCs, exploitation in the wild, and other factors. See: https://www.first.org/epss/model
-
- CISA Known Exploited Vulnerability (KEV): The CISA KEV is a catalog of the most critical vulnerabilities that are known to have been exploited by attackers in the wild. See: https://www.cisa.gov/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog
- Continuous Usage Based Scoring: Applications under intensive use are at a higher priority for patching since their exposure time is increased vs. applications that are infrequently used or unused. Morphisec’s continuous usage scoring drives remediation efforts based on the organization’s actual environment and active processes.
- Patchless Protection and Threat Prevention using Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD): Morphisec AMTD protects application memory, prevents malicious memory exploitation, and malicious access to system APIs, processes and resources, providing compensating controls to protect applications from exploitation until security patches are applied.
Use Cases driven by Morphisec Vulnerability Prioritization
- Risk and exposure management — Application usage across organizations vary. No two organizations have the same risk profile. For example, if an application is unused, the attack surface of a severe vulnerability shrinks to near zero, and the risk of a successful exploit shrinks with it. On the other hand, a lower severity vulnerability in a widely used application creates a larger attack surface and greater risk of exploit.
- Patching gaps – Vulnerability remediation is a resource intensive process, leading to time gaps where organizations are exposed. Deploying security patches requires testing, compatibility checks, risk assessment leading to a lead time gap of 4-6 week and more to patching a vulnerability. Prioritization and speeds are crucial in this cycle to mitigate exposure before the rise of new security risks.
- Compliance – Regulatory standards and compliance requirements mandate patch management protocols and reporting to ensure companies mitigate risk through broader vulnerability management. However, keeping pace with patch management is an operational nightmare for IT and security teams. Ever-increasing vulnerability volumes are impossible for teams to address in a timely fashion, leaving them at risk of exploitation.
Morphisec’s Vulnerability Prioritization Vs. Common Vulnerability Management Practices
|
Capability |
Common Vulnerability Management Practices |
Morphisec Vulnerability Prioritization |
|
Hosts & Business Function Risk Prioritization |
❌ |
✓ |
|
Application Driven Risk Prioritization |
❌ |
✓ |
|
Usage based Risk Prioritization |
❌ |
✓ |
|
Vulnerability Scoring Method |
Primarily CVSS |
CVSS + CISA KEV + EPSS + Usage |
|
Vulnerability Assessment Intervals |
Periodical / On-Demand Scans |
Continuous / Runtime Visibility |
|
Patchless Protection / Compensating Controls |
❌ |
Virtual Patching Powered by Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD) |
|
Threat Prevention |
Varies by offering |
Advanced Threat and Ransomware Prevention Powered by Automated Moving Target Defense (AMTD) |
 Risk-based vulnerability prioritization capabilities take risk and exposure management to the next level, helping customers reduce total cost of ownership. Morphisec enables security teams to prioritize patching efforts with multiple strategies – business context, host scoring, application-driven risk prioritization, and exploitability metrics while considering the actual usage of applications within the organization.
Risk-based vulnerability prioritization capabilities take risk and exposure management to the next level, helping customers reduce total cost of ownership. Morphisec enables security teams to prioritize patching efforts with multiple strategies – business context, host scoring, application-driven risk prioritization, and exploitability metrics while considering the actual usage of applications within the organization.
Morphisec’s prevention-first security (powered by AMTD) uses a patented zero-trust at-execution technology to proactively block advanced and evasive attacks. As an application loads to memory space, the platform’s three-step prevention process uses its AMTD technology to morph and conceal process structures, protecting code memory and uses lightweight skeleton traps to deceive attackers. Unable to access original resources, malicious code injection fails, thereby stopping and logging attacks with full forensic details.
By combining next generation vulnerability prioritization with the power of AMTD, organizations can better support exposure management and risk management initiatives with the ability to measure, analyze, mitigate and communicate cyber risk in real-time.
Book a demo to see Morphisec AMTD and risk-based vulnerability prioritization in action.




.png?width=571&height=160&name=iso27001-(2).png)